Building Automation Systems
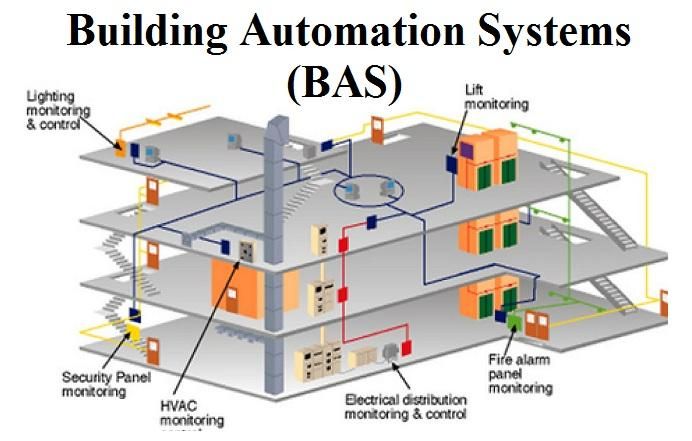
Building Automation Systems (BAS), also known as Building Management Systems (BMS) or Building Control Systems (BCS), are integrated networks of software and hardware that control and monitor various building functions. These systems optimize energy efficiency, security, comfort, and safety within commercial, industrial, and residential structures. BAS manages functions like heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, access control, and fire safety.
Key components of building automation systems include sensors, controllers, actuators, and communication networks. These systems collect data, analyze it, and make real-time adjustments to building parameters, reducing energy consumption, operational costs, and environmental impact.
Building automation systems are instrumental in achieving sustainability goals, enhancing occupant comfort, and complying with regulations. They provide centralized control and remote monitoring, allowing building managers to make informed decisions and respond promptly to alarms or system malfunctions.
Building Automation Systems: The Future of Smart Structures
In a world driven by technological innovation, our buildings are becoming smarter than ever before. Building Automation Systems (BAS) are at the forefront of this transformation, revolutionizing the way we design, construct, and manage structures. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the world of BAS, delving into its significance, key components, applications, and the profound impact it has on the future of architecture and engineering.
The Essence of Building Automation Systems
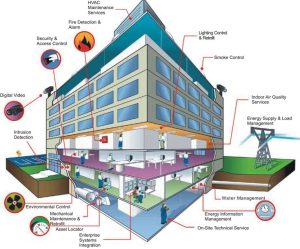
Building Automation Systems, often referred to as Building Management Systems (BMS) or Energy Management Systems (EMS), are centralized networks of interconnected devices and software that control and monitor various building operations. These operations can include heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and more. The goal is to optimize building performance, enhance occupant comfort, and reduce energy consumption. Don’t Forget to Check Out Our Website: unibrowses
Key Components and Technologies
At the core of BAS are a multitude of technologies and components. These include sensors, actuators, controllers, and software platforms. They communicate with each other and with the building’s systems, collecting data and making real-time adjustments to ensure efficiency and sustainability.
Understanding Building Automation Systems
BAS offer a wide array of advantages and benefits, making them an indispensable part of modern architecture and engineering.
Energy Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of BAS is their ability to significantly improve energy efficiency. By monitoring and controlling energy-consuming systems, BAS can reduce energy wastage and lower utility costs.
Enhanced Comfort and Security
BAS enhance occupant comfort by maintaining optimal indoor conditions, such as temperature and lighting. They also contribute to building security by providing surveillance, access control, and alarm systems.
Sustainability
In an era of increasing environmental awareness, BAS play a crucial role in sustainability efforts. They help reduce a building’s carbon footprint by optimizing energy usage and minimizing resource consumption.
Cost Savings
BAS can lead to substantial cost savings in the long run. By automating processes and reducing energy expenditures, building owners and managers can enjoy a rapid return on investment.
Applications of Building Automation Systems
BAS are versatile and find applications across various types of buildings and facilities.
Commercial Buildings
In commercial buildings, such as offices and retail spaces, BAS help maintain a comfortable environment for employees and customers while reducing operating costs.

Residential Spaces
BAS are making their way into residential homes, enabling homeowners to control heating, cooling, lighting, and security systems with ease.
Healthcare Facilities
In healthcare settings, BAS ensure precise environmental conditions for patient comfort and safety while optimizing energy usage.
Industrial Complexes
Industrial facilities benefit from BAS by streamlining operations, enhancing security, and meeting strict regulatory requirements.
Challenges and Considerations
While BAS offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain challenges and considerations.
Data Security
The interconnected nature of BAS raises concerns about data security. Protecting sensitive information and preventing cyberattacks are paramount.
Integration Complexities
Integrating BAS with existing building systems can be complex and may require retrofitting. Careful planning is essential to ensure seamless integration.
Maintenance and Training
Regular maintenance and training for building operators and maintenance staff are crucial to ensure the continued effectiveness of BAS.
Future Trends in BAS
As technology continues to advance, several trends are shaping the future of BAS.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML technologies are being incorporated into BAS, enabling systems to learn and adapt to building occupants’ preferences and optimize energy usage further.
Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
BAS are increasingly integrating with IoT devices, allowing for more data collection and automation possibilities.
Human-Centric Design
Future BAS will prioritize occupant well-being by focusing on human-centric design, ensuring optimal comfort and health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Building Automation Systems are not merely a technological advancement; they are a fundamental shift in how we design, construct, and manage our built environment. As BAS continue to evolve,
FAQs
Q. What exactly are Building Automation Systems (BAS)?
A. Building Automation Systems (BAS), also known as Building Management Systems (BMS) or Energy Management Systems (EMS), are centralized networks of interconnected devices and software used to control and monitor various building operations, such as heating, ventilation, air conditioning (HVAC), lighting, security, and more.
Q. What are the primary advantages of using BAS in buildings?
A. BAS offer several advantages, including improved energy efficiency, enhanced occupant comfort, increased security, sustainability, and cost savings through optimized building operations.
Q. In which types of buildings and facilities are BAS commonly used?
A. BAS are versatile and find applications in various settings, including commercial buildings (offices and retail spaces), residential homes, healthcare facilities, and industrial complexes.
Q. What are the key challenges associated with implementing BAS?
A. Challenges in implementing BAS include data security concerns, integration complexities with existing building systems, and the need for regular maintenance and staff training to ensure continued effectiveness.